PID控制器原理 v2.1
本库实现的PID控制器的传递函数为:
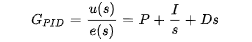
连续PID被转换到离散域,可以描述为三个部分的总和:

比例部分:
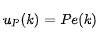
积分部分:
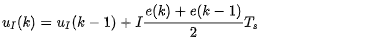
微分部分:
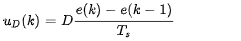
其中,u(k)是时刻k的控制信号(在我们的例子中是电压Uq),e(k)、e(k-1)是当前时刻k和前一步k-1的跟踪误差。跟踪误差是目标速度值vd和测量速度v之间的差值。
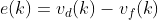
实现细节
PID算法在SimpleFOC库中通过PIDController类实现。实例化该类时需要指定参数。
PIDController(float P, float I, float D, float ramp, float limit);
该类只有一个函数:
// PID controller function
float PIDController::operator() (float error){
// calculate the time from the last call
unsigned long timestamp_now = _micros();
float Ts = (timestamp_now - timestamp_prev) * 1e-6;
// quick fix for strange cases (micros overflow)
if(Ts <= 0 || Ts > 0.5) Ts = 1e-3;
// u(s) = (P + I/s + Ds)e(s)
// Discrete implementations
// proportional part
// u_p = P *e(k)
float proportional = P * error;
// Tustin transform of the integral part
// u_ik = u_ik_1 + I*Ts/2*(ek + ek_1)
float integral = integral_prev + I*Ts*0.5*(error + error_prev);
// antiwindup - limit the output voltage_q
integral = _constrain(integral, -limit, limit);
// Discrete derivation
// u_dk = D(ek - ek_1)/Ts
float derivative = D*(error - error_prev)/Ts;
// sum all the components
float output = proportional + integral + derivative;
// antiwindup - limit the output variable
output = _constrain(output, -limit, limit);
// limit the acceleration by ramping the output
float output_rate = (output - output_prev)/Ts;
if (output_rate > output_ramp)
output = output_prev + output_ramp*Ts;
else if (output_rate < -output_ramp)
output = output_prev - output_ramp*Ts;
// saving for the next pass
integral_prev = integral;
output_prev = output;
error_prev = error;
timestamp_prev = timestamp_now;
return output;
}
因此,你可以很容易地将PID集成到你的代码中。
void setup(){
...
PIDController some_pid = PIDController{.....};
...
}
void loop(){
float control = some_pid(target-measurement);
}
这个PID类在BLDCMotor和StepperMotor类中实现,用于处理运动控制的速度(motor.PID_velocity)和位置(motor.P_angle)。你可以通过修改这些PID控制器的公共变量来改变它们的参数:
// PID controller configuration structure
class PIDController
{
.....
float P; //!< Proportional gain
float I; //!< Integral gain
float D; //!< Derivative gain
....
};
例如:
motor.PID_velocity.P = 1;
motor.P_angle.P = 10;
