速度控制示例
使用 HMBGC V2.2 板
这是一个使用 FOC 算法的非常简单且很棒的示例,采用云台控制器板。它们本不打算用于闭环位置控制,但 简易FOC库 不仅让这成为可能,而且还相当简单。
以下是我们在这个项目中使用的硬件:
连接所有部件
有关 HMBGC V2.2 连接的更深入解释,请查看 连接示例。
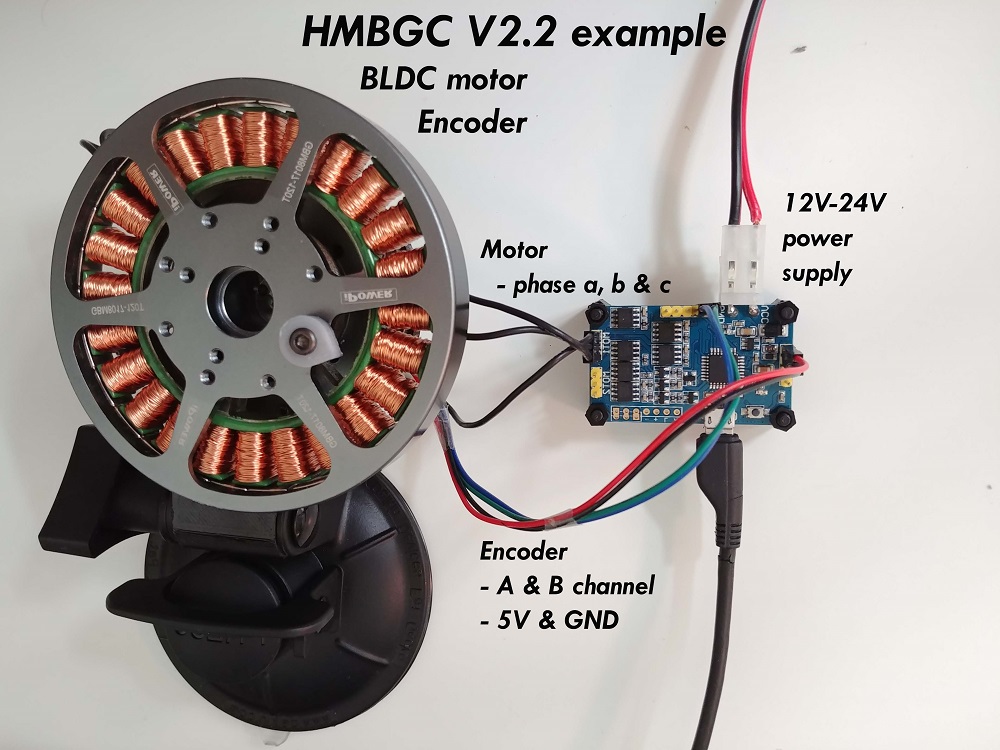
编码器
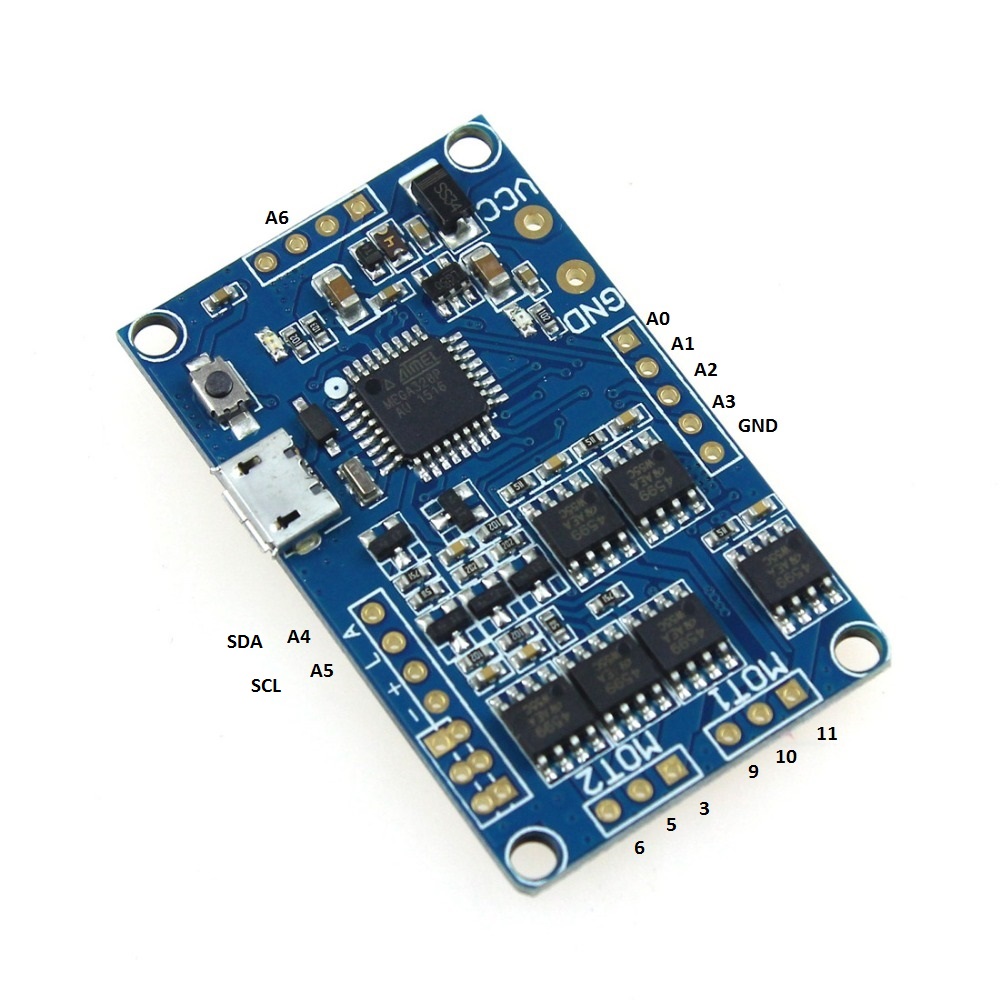
引脚限制
HMBGC 无法访问 Arduino 的外部中断引脚2和3,而且我们唯一可以访问的引脚是模拟引脚A0-A7。 因此,我们需要使用软件中断库来读取编码器通道,更多信息请查看编码器 代码实现。
- 编码器通道
A和B连接到引脚A0和A1。
电机
- 电机相
a、b和c直接连接到驱动器输出 - 电机端子
M1使用 Arduino 引脚9、10、11,M2使用3、5、6
Arduino 代码
让我们浏览这个示例的完整代码并一起编写。 首先,你需要包含 SimpleFOC 库:
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
确保你已经安装了该库。如果你还没有安装,请查看 入门页面。
另外,对于像 HMBGC 这样的云台控制器,我们无法访问硬件中断引脚,所以你需要一个软件中断库。 我建议使用 PciManager 库。如果你还没有安装它,可以直接通过 Arduino 库管理器进行安装。更多信息请查看 Encoder 类 文档。 安装好后,请将其包含到草图中:
// software interrupt library
#include <PciManager.h>
#include <PciListenerImp.h>
编码器代码
首先,我们定义 Encoder 类,包含 A 和 B 通道引脚以及每转脉冲数。
// define Encoder
Encoder encoder = Encoder(A0, A1, 2048);
然后我们定义缓冲回调函数。
// channel A and B callbacks
void doA(){encoder.handleA();}
void doB(){encoder.handleB();}
接下来我们定义 PciManager 引脚变化监听器:
// pin change listeners
PciListenerImp listenerA(encoder.pinA, doA);
PciListenerImp listenerB(encoder.pinB, doB);
在 setup() 函数中,首先初始化编码器:
// initialize encoder hardware
encoder.init();
并且,代替调用 encoder.enableInterrupt() 函数,我们使用 PciManager 库接口来附加中断。
// interrupt initialization
PciManager.registerListener(&listenerA);
PciManager.registerListener(&listenerB);
就这样,我们来设置电机。
有关编码器的更多配置参数,请查看 Encoder 类 文档。电机代码
首先,我们需要定义 BLDCMotor 类,并指定极对数(14)
// define BLDC motor
BLDCMotor motor = BLDCMotor(14);
如果你不确定你的极对数是多少,请查看 find_pole_pairs.ino 示例。接下来,我们需要定义 BLDCDriver3PWM 类,包含电机的 PWM 引脚号
// define BLDC driver
BLDCDriver3PWM driver = BLDCDriver3PWM(9, 10, 11);
然后在 setup() 中,如果电源电压不是 12 伏,首先配置电源电压并初始化驱动器。
// power supply voltage
// default 12V
driver.voltage_power_supply = 12;
driver.init();
然后,我们通过指定 motor.controller 变量来告诉电机运行哪个控制环。
// set control loop type to be used
// MotionControlType::torque
// MotionControlType::velocity
// MotionControlType::angle
motor.controller = MotionControlType::velocity;
现在我们配置 PI 控制器参数
// velocity PI controller parameters
// default P=0.5 I = 10
motor.PID_velocity.P = 0.2;
motor.PID_velocity.I = 20;
// jerk control using voltage voltage ramp
// default value is 300 volts per sec ~ 0.3V per millisecond
motor.PID_velocity.output_ramp = 1000;
//default voltage_power_supply
motor.voltage_limit = 6;
此外,我们可以配置低通滤波器时间常数 Tf
// velocity low pass filtering
// default 5ms - try different values to see what is the best.
// the lower the less filtered
motor.LPF_velocity.Tf = 0.01;
有关速度控制环参数的更多信息,请查看 文档。
最后,我们将编码器和驱动器连接到电机,进行硬件初始化和磁场定向控制初始化。
// link the motor to the sensor
motor.linkSensor(&encoder);
// link driver
motor.linkDriver(&driver);
// initialize motor
motor.init();
// align encoder and start FOC
motor.initFOC();
电机代码中最后一个重要部分当然是 loop 函数中的 FOC 程序。
void loop() {
// iterative FOC function
motor.loopFOC();
// iterative function setting and calculating the velocity loop
// this function can be run at much lower frequency than loopFOC function
motor.move(target_velocity);
}
就这样,现在让我们看看完整的代码!
有关更多配置参数和控制环,请查看 BLDCMotor 类 文档。完整的 Arduino 代码
在完整代码中,我添加了一个小型串行 命令器接口,以便能够实时更改速度目标值。
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
// software interrupt library
#include <PciManager.h>
#include <PciListenerImp.h>
// define BLDC motor
BLDCMotor motor = BLDCMotor( 14 );
// define driver
BLDCDriver3PWM driver = BLDCDriver3PWM(9, 10, 11);
// define Encoder
Encoder encoder = Encoder(A0, A1, 500);
// interrupt routine initialization
void doA(){encoder.handleA();}
void doB(){encoder.handleB();}
// encoder interrupt init
PciListenerImp listenerA(encoder.pinA, doA);
PciListenerImp listenerB(encoder.pinB, doB);
// target variable
float target_velocity=0;
// commander interface
Commander command = Commander(Serial);
void onTarget(char* cmd){ command.scalar(&target_velocity, cmd); }
void setup() {
// initialize encoder hardware
encoder.init();
// interrupt initialization
PciManager.registerListener(&listenerA);
PciManager.registerListener(&listenerB);
// link the motor to the sensor
motor.linkSensor(&encoder);
// power supply voltage
// default 12V
driver.voltage_power_supply = 12;
driver.init();
// link the motor to the driver
motor.linkDriver(&driver);
// set FOC loop to be used
// MotionControlType::torque
// MotionControlType::velocity
// MotionControlType::angle
motor.controller = MotionControlType::velocity;
// controller configuration based on the control type
// velocity PI controller parameters
// default P=0.5 I = 10
motor.PID_velocity.P = 0.2;
motor.PID_velocity.I = 20;
// jerk control using voltage voltage ramp
// default value is 300 volts per sec ~ 0.3V per millisecond
motor.PID_velocity.output_ramp = 1000;
// velocity low pass filtering
// default 5ms - try different values to see what is the best.
// the lower the less filtered
motor.LPF_velocity.Tf = 0.01;
//default voltage_power_supply
motor.voltage_limit = 6;
// initialize motor
motor.init();
// align encoder and start FOC
motor.initFOC();
// add target command T
command.add('T', onTarget, "target velocity");
// monitoring port
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Motor ready.");
Serial.println("Set the target velocity using serial terminal:");
_delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
// iterative FOC function
motor.loopFOC();
// 0.5 hertz sine wave
//target_velocity = sin( micros()*1e-6 *2*M_PI * 0.5 );
motor.move(target_velocity);
// iterative function setting the velocity target
command.run();
}



