On this page
Stepper motor control example
using L298N and Stm32 Nucleo-64
For this stepper motor control example we are going to be using this hardware:
Download the STL file as well as STEP and solidworks project of the amt103 mount on the nema17 used in the images and the Youtube video here.
Connecting everything together
Here is an example of the connection scheme using the L298N and Nucleo-64:
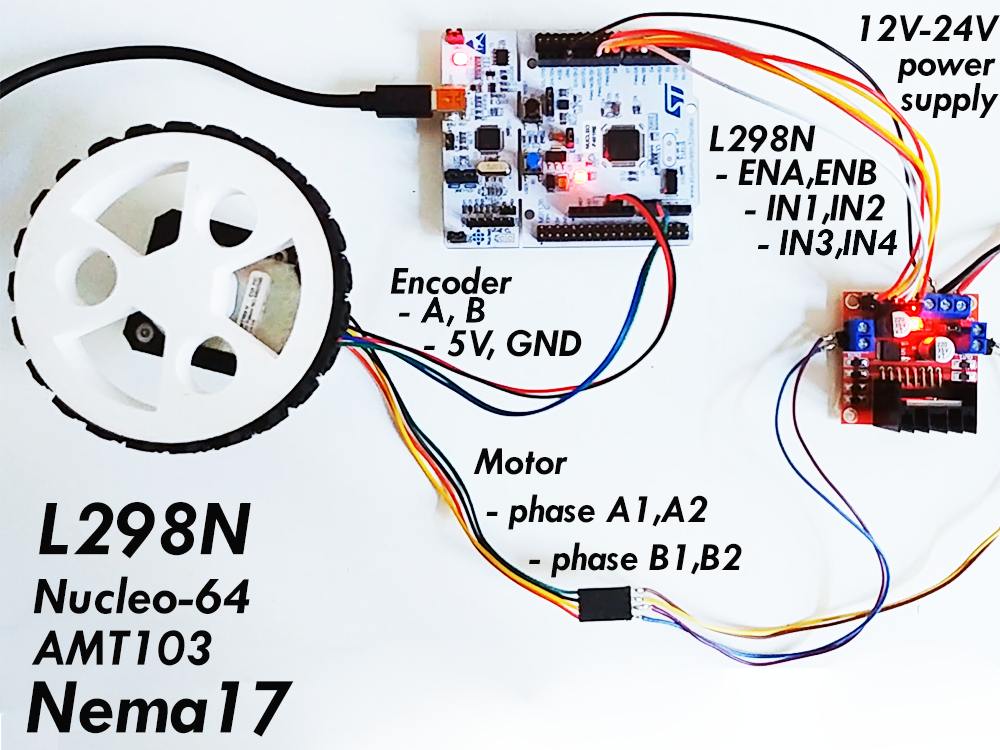
L298N
- Channels
ENAandENBare connected to pins7and8 - Channels
IN1,IN2,IN3andIN4are connected to the pins5,6,9,10 - Common ground is connected in between nucleo and L298N
- 12V power-supply is connected directly to the driver
Encoder
- Channels
AandBare connected to the pinsA0qndA1 - Index channel is not used in this example but you can easily modify this example to support it
Motor
- Motor phases
A1,A2,B1andB2are connected directly the motor connectors of the L298N chip.
Full Arduino code
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
// Stepper motor instance
StepperMotor motor = StepperMotor(50);
// Stepper driver instance
StepperDriver4PWM driver = StepperDriver4PWM(5, 6, 9, 10, 8, 7);
// encoder instance
Encoder encoder = Encoder(A1, A2, 2048);
// channel A and B callbacks
void doA(){encoder.handleA();}
void doB(){encoder.handleB();}
// commander interface
Commander command = Commander(Serial);
void onMotor(char* cmd){ command.motor(&motor, cmd); }
void setup() {
// initialize encoder sensor hardware
encoder.init();
encoder.enableInterrupts(doA, doB);
// link the motor to the sensor
motor.linkSensor(&encoder);
// choose FOC modulation
motor.foc_modulation = FOCModulationType::SpaceVectorPWM;
// power supply voltage [V]
driver.voltage_power_supply = 12;
driver.init();
// link the motor to the sensor
motor.linkDriver(&driver);
// set control loop type to be used
motor.controller = MotionControlType::torque;
// controller configuration based on the control type
motor.PID_velocity.P = 0.2;
motor.PID_velocity.I = 20;
motor.PID_velocity.D = 0;
// default voltage_power_supply
motor.voltage_limit = 12;
// velocity low pass filtering time constant
motor.LPF_velocity.Tf = 0.01;
// angle loop controller
motor.P_angle.P = 20;
// angle loop velocity limit
motor.velocity_limit = 50;
// use monitoring with serial for motor init
// monitoring port
Serial.begin(115200);
// comment out if not needed
motor.useMonitoring(Serial);
// initialise motor
motor.init();
// align encoder and start FOC
motor.initFOC();
// set the initial target value
motor.target = 2;
// define the motor id
command.add('M', onMotor, "motor");
// Run user commands to configure and the motor (find the full command list in docs.simplefoc.com)
Serial.println(F("Motor commands sketch | Initial motion control > torque/voltage : target 2V."));
_delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
// iterative setting FOC phase voltage
motor.loopFOC();
// iterative function setting the outter loop target
// velocity, position or voltage
// if tatget not set in parameter uses motor.target variable
motor.move();
// user communication
command.run();
}