On this page
Position control example
using SimpleFOCMini
For this BLDC motor position control example we are going to be using this hardware:
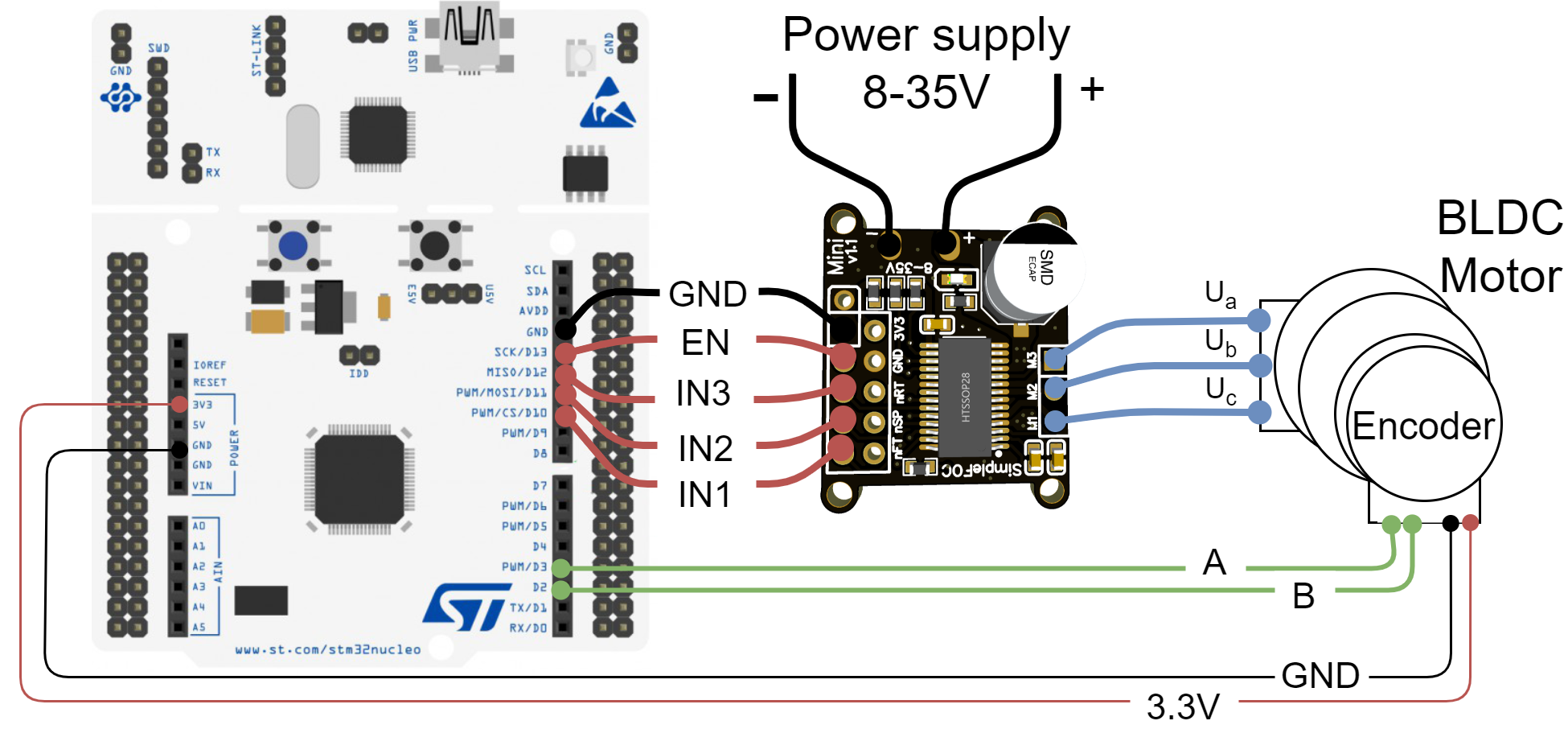
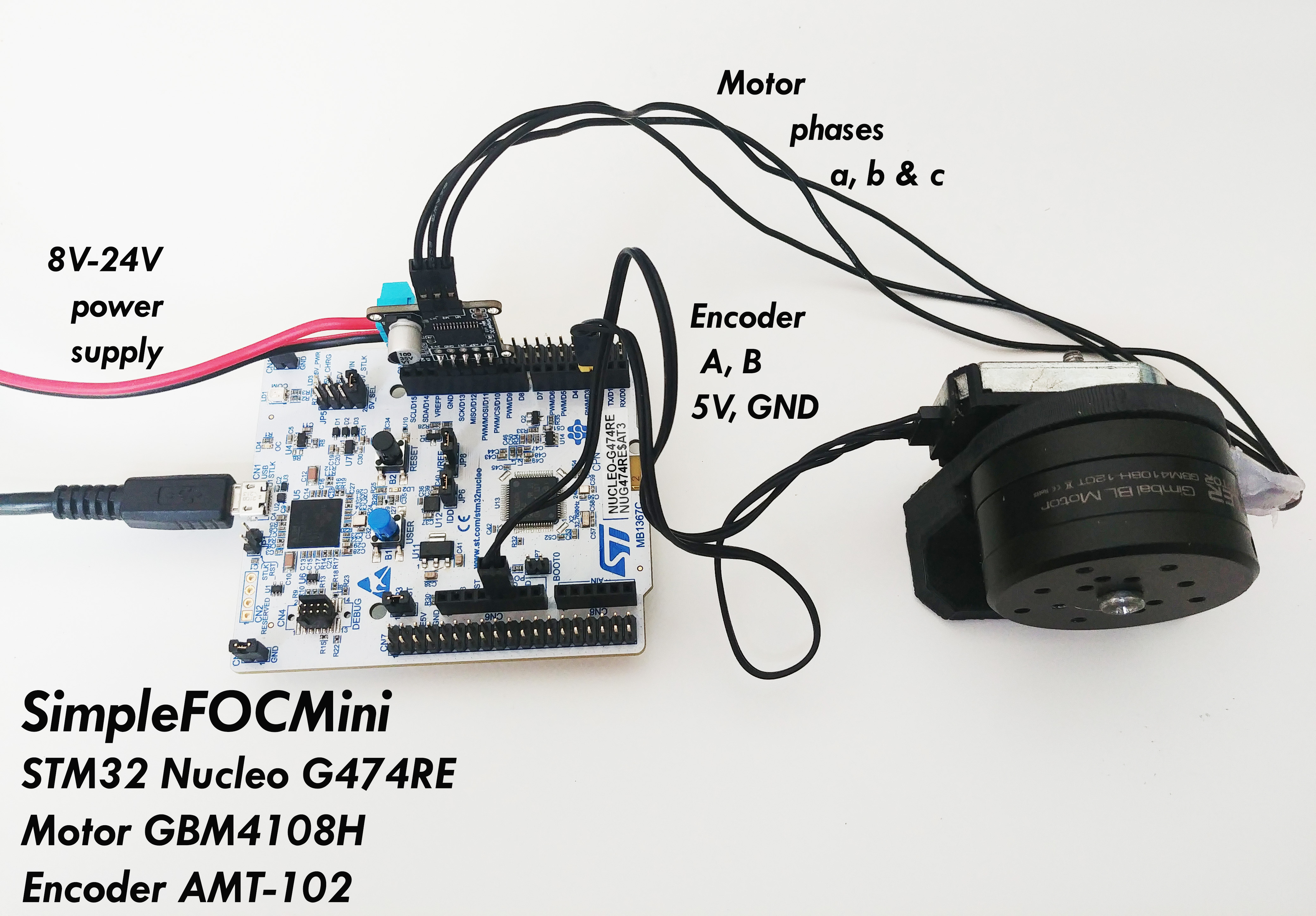
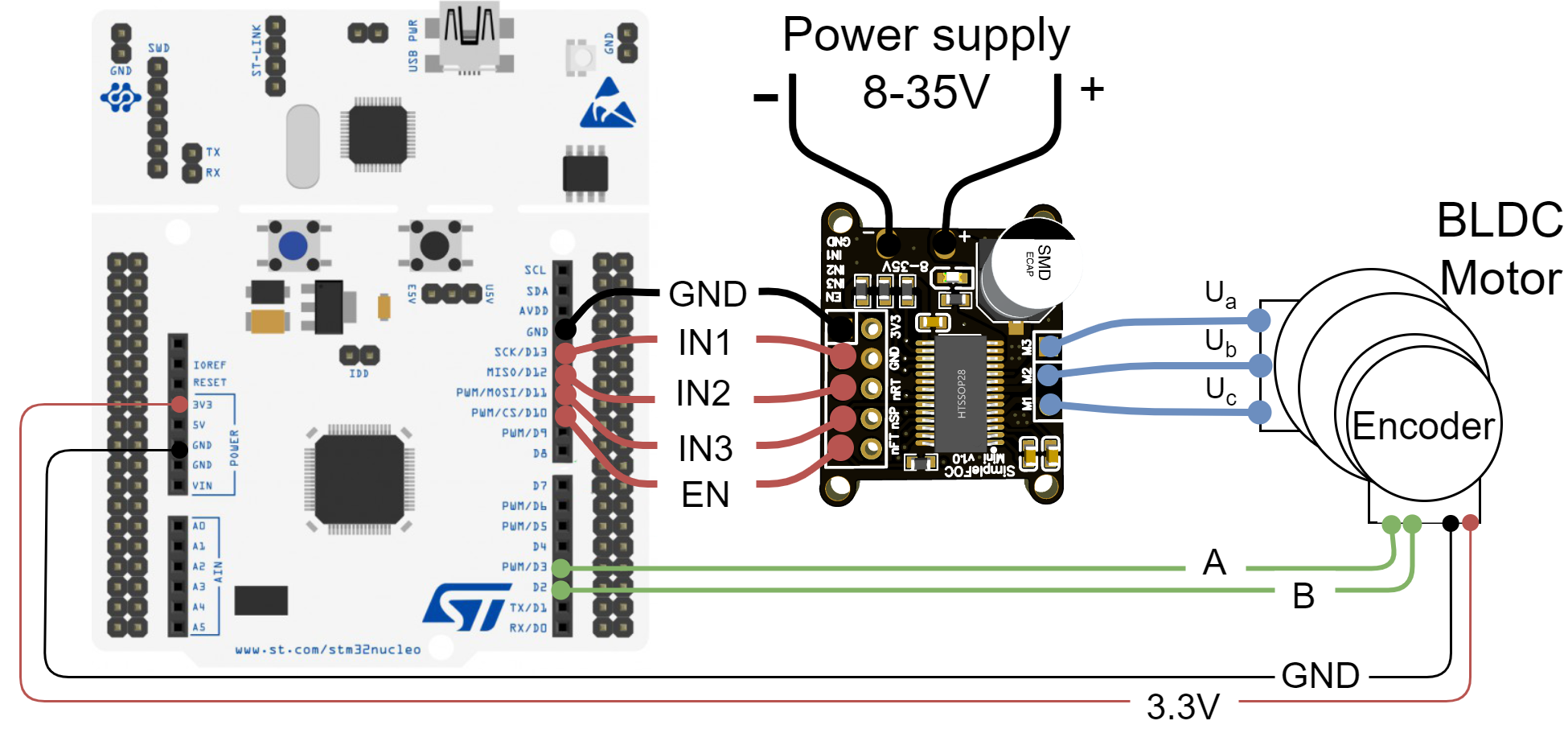
Connecting everything together
For more information about the SimpleFOCMini check the docs. Currently, there are two versions of the SimpleFOCMini board available v1.0 and v1.1. The main difference between the two versions is the order of the pins. This example can be used with both versions of the board, however there are slight differences in the pinout.
Choose your SimpleFOCMini version:
SimpleFOCMini V1.0 SimpleFOCMini V1.1
Encoder
- Channels
AandBare connected to the Arduino UNO pins2and3.
Motor
- Motor phases
a,bandcare connected directly the motor terminal connector connectorsM1,M2andM3of the SimpleFOCMini board
SimpleFOCMini
SimpleFOCMini V1.0 SimpleFOCMini V1.1
- The most convenient way of plugging the SimpleFOCMini board to the Nucleo board is to stack it on its pins
10-13.GND-GNDIN1-13IN2-12IN3-11EN-10
Arduino code
Let’s go through the full code for this example and write it together. First thing you need to do is include the SimpleFOC library:
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
Make sure you have the library installed. If you still don’t have it please check the get started page
Encoder code
First we define the Encoder class with the A and B channel pins and number of impulses per revolution.
// define Encoder
Encoder encoder = Encoder(2, 3, 2048);
Then we define the buffering callback functions.
// channel A and B callbacks
void doA(){encoder.handleA();}
void doB(){encoder.handleB();}
In the setup() function we initialize the encoder and enable interrupts:
// initialize encoder hardware
encoder.init();
// hardware interrupt enable
encoder.enableInterrupts(doA, doB);
And that is it, let’s setup the motor.
For more configuration parameters of the encoders please check the Encoder class docs. Motor code
SimpleFOCMini V1.0 SimpleFOCMini V1.1
First we need to define the BLDCMotor class with the number od pole pairs (11)
// define BLDC motor
BLDCMotor motor = BLDCMotor(11);
If you are not sure what your pole pairs number is please check the find_pole_pairs.ino example. Next we need to define the BLDCDriver3PWM class with the PWM pin numbers of the motor and the driver enable pin
// define BLDC driver
BLDCDriver3PWM driver = BLDCDriver3PWM(13, 12, 11, 10);
Then in the setup() we configure first the voltage of the power supply if it is not 12 Volts and init the driver.
// power supply voltage
// default 12V
driver.voltage_power_supply = 12;
driver.init();
Then we tell the motor which control loop to run by specifying the motor.controller variable.
// set control loop type to be used
// MotionControlType::torque
// MotionControlType::velocity
// MotionControlType::angle
motor.controller = MotionControlType::angle;
Now we configure the velocity PI controller parameters
// velocity PI controller parameters
// default P=0.5 I = 10
motor.PID_velocity.P = 0.2;
motor.PID_velocity.I = 20;
//default voltage_power_supply
motor.voltage_limit = 6;
Additionally we can configure the Low pass filter time constant Tf
// velocity low pass filtering
// default 5ms - try different values to see what is the best.
// the lower the less filtered
motor.LPF_velocity.Tf = 0.02;
Finally we configure position P controller gain and the velocity limit variable.
// angle P controller
// default P=20
motor.P_angle.P = 20;
// maximal velocity of the position control
// default 20
motor.velocity_limit = 4;
For more information about the angle control loop parameters please check the doc.
Next we connect the encoder and the driver to the motor, do the hardware init and init of the Field Oriented Control.
// link the motor to the sensor
motor.linkSensor(&encoder);
// link the motor to the driver
motor.linkDriver(&driver);
// initialize motor
motor.init();
// align encoder and start FOC
motor.initFOC();
The last peace of code important for the motor is of course the FOC routine in the loop function.
void loop() {
// iterative FOC function
motor.loopFOC();
// iterative function setting and calculating the angle/position loop
// this function can be run at much lower frequency than loopFOC function
motor.move();
}
That is it, let’s see the full code now!
For more configuration parameters and control loops please check the BLDCMotor class doc. Full Arduino code
To the full code I have added a small serial commander interface, to be able to change position/angle target value in real time.
SimpleFOCMini V1.0 SimpleFOCMini V1.1
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
// init BLDC motor
BLDCMotor motor = BLDCMotor( 11 );
// init driver
BLDCDriver3PWM driver = BLDCDriver3PWM(13, 12, 11, 10);
// init encoder
Encoder encoder = Encoder(2, 3, 2048);
// channel A and B callbacks
void doA(){encoder.handleA();}
void doB(){encoder.handleB();}
// commander interface
Commander command = Commander(Serial);
void onTarget(char* cmd){ command.motion(&motor, cmd); }
void setup() {
// initialize encoder hardware
encoder.init();
// hardware interrupt enable
encoder.enableInterrupts(doA, doB);
// link the motor to the sensor
motor.linkSensor(&encoder);
// power supply voltage
// default 12V
driver.voltage_power_supply = 12;
driver.init();
// link the motor to the driver
motor.linkDriver(&driver);
// set control loop to be used
motor.controller = MotionControlType::angle;
// controller configuration based on the control type
// velocity PI controller parameters
// default P=0.5 I = 10
motor.PID_velocity.P = 0.2;
motor.PID_velocity.I = 20;
//default voltage_power_supply
motor.voltage_limit = 6;
// velocity low pass filtering
// default 5ms - try different values to see what is the best.
// the lower the less filtered
motor.LPF_velocity.Tf = 0.02;
// angle P controller
// default P=20
motor.P_angle.P = 20;
// maximal velocity of the position control
// default 20
motor.velocity_limit = 4;
// initialize motor
motor.init();
// align encoder and start FOC
motor.initFOC();
// add target command T
command.add('T', doTarget, "motion control");
// monitoring port
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Motor ready.");
Serial.println("Set the target angle using serial terminal:");
_delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
// iterative FOC function
motor.loopFOC();
// function calculating the outer position loop and setting the target position
motor.move();
// commander interface with the user
commander.run();
}