On this page
Stepper motor control example
using the SimpleFOCShield and Stm32 Nucleo-64
For this stepper motor control example we are going to be using this hardware:
Download the STL file as well as STEP and solidworks project of the amt103 mount on the nema17 used in the images and the Youtube video here.
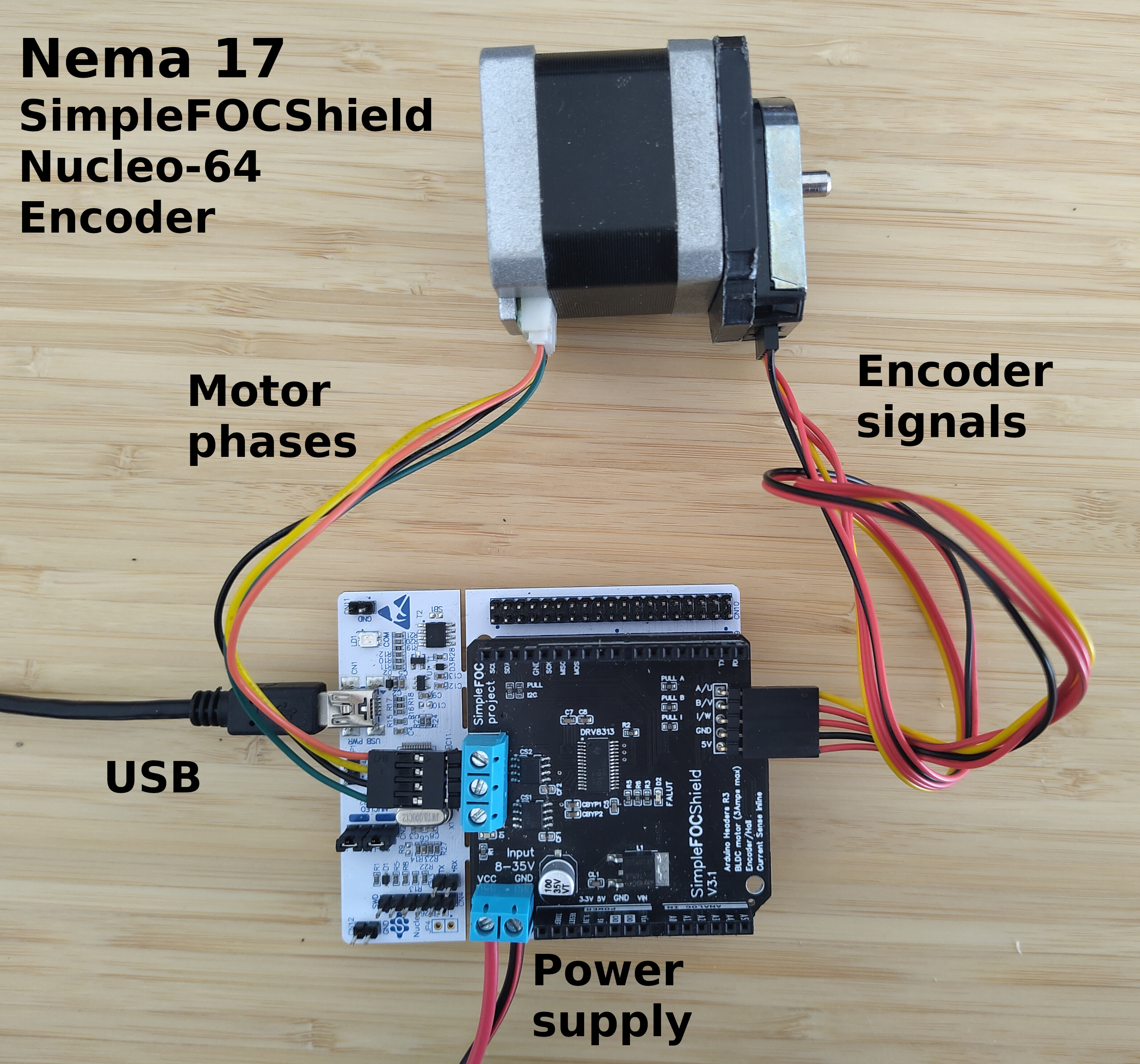
Connecting everything together
Here is an example of the connection scheme using the SimpleFOCShield and Nucleo-64:
Nema 17 stepper motor connection using 3 phases
As nema 17 steppers have 2 phases and 4 wires, we need to transform them to 3 phases to connect them to the SimpleFOCShiled. So we will connect one wire from each phase to the shield spearately and the third wire of each phase will be connected together to the common phase.
| Pin | Nema 17 wire | Shield phase |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A+ | A |
| 2 | B-, A- | B |
| 3 | B+ | C |
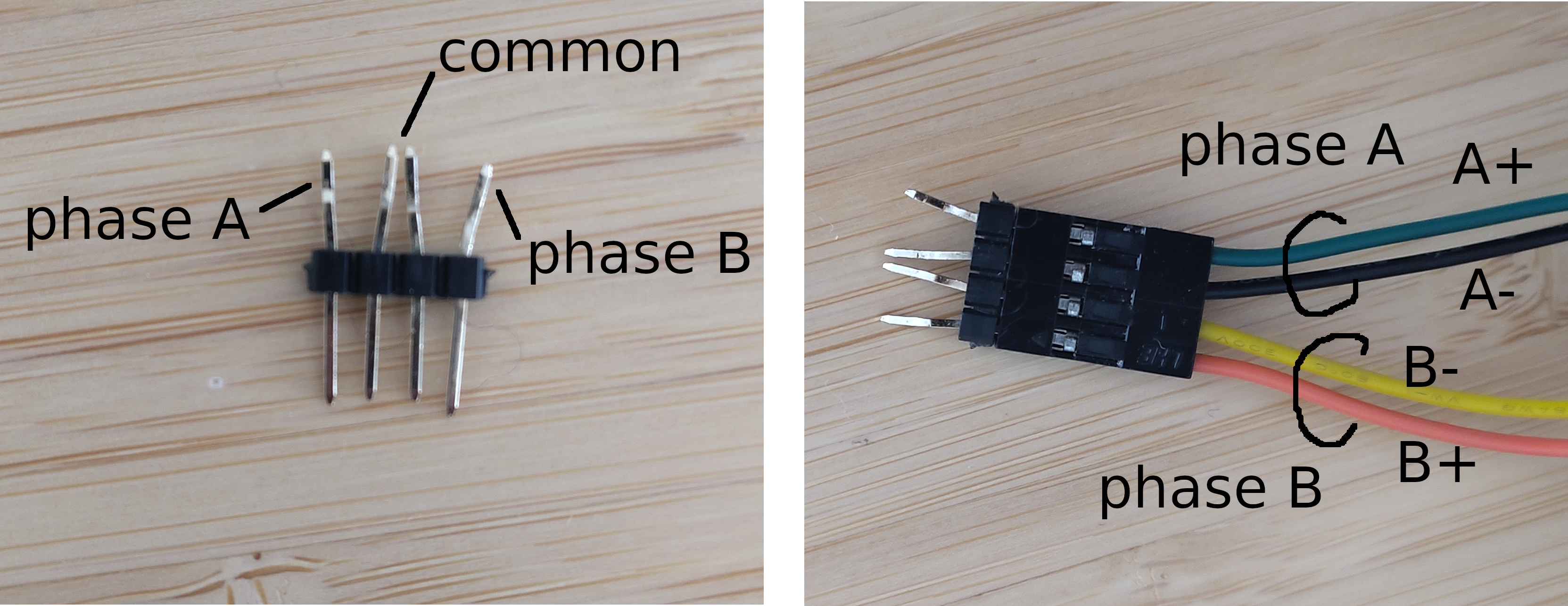
- Motor phases
A,Band common are connected directly the motor terminal connectorTB_M1
It is not too important which of the two wires
+or-you connect to which pin as long as the common pin2has the wires of both phases connected to it. If it does not the motor will not work.
SimpleFOCShield connections
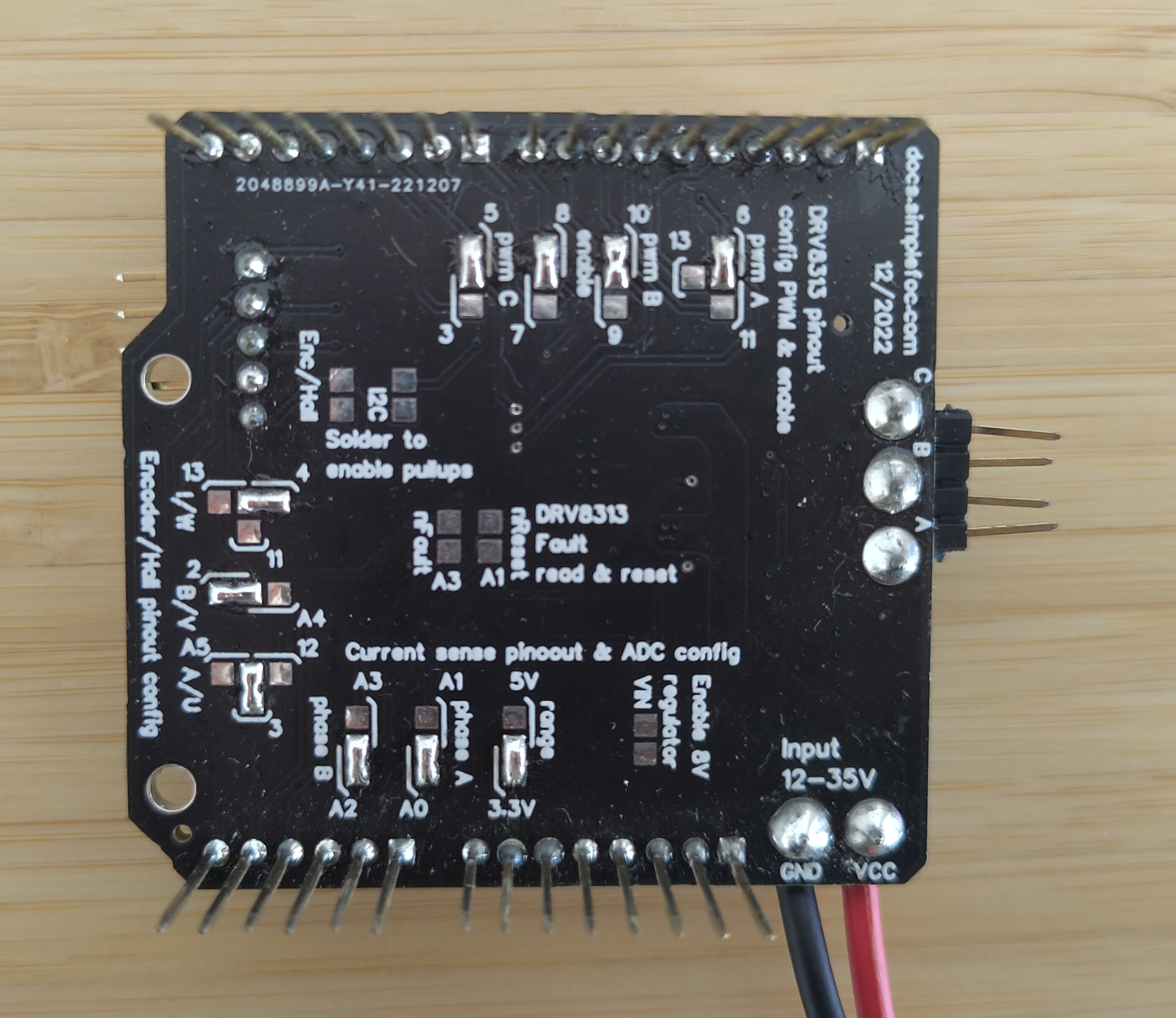
| Signal | Pwm A | Pwm B | Pwm C | Enable | Encoder A | Encoder B | Encoder I | Current A | Current B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin | 6 | 10 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 4 | A0 | A2 |
Encoder
- Channels
AandBare connected to the encoder connectorP_ENC, terminalsAandB. - Index channel you can connect directly to the
P_ENCas well to the terminalI
Arduino code
There are just a couple of things to note when using stepper motors in the hybrid configuration with the SimpleFOClibrary:
- The motor is configured as a
HybridStepperMotorand not aStepperMotor
HybridStepperMotor motor = HybridStepperMotor(50);
- The driver pins order is important, it should be:
AphaseBphase- common pin In this example we are using the
BLDCDriver3PWMdriver
// IMPORTANT: the order of the pins is important, it should be:
// 1. Stepper A phase (shield pin A)
// 2. Stepper B phase (shield pin C)
// 3. common pin (shield pin B)
BLDCDriver3PWM driver = BLDCDriver3PWM(6, 5, 10, 8);
Here is the full code example for the stepper motor control using the SimpleFOCShield and Stm32 Nucleo-64:
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
// Stepper motor
HybridStepperMotor motor = HybridStepperMotor(50);
// BLDC driver instance
// SimpleFOCShield
BLDCDriver3PWM driver = BLDCDriver3PWM(6, 5, 10, 8);
// encoder instance
Encoder encoder = Encoder(2, 3, 2048);
// channel A and B callbacks
void doA(){encoder.handleA();}
void doB(){encoder.handleB();}
// inline current sensor instance
// ACS712-05B has the resolution of 0.185mV per Amp
// NOTE: LowsideCurrentSense sense is used because its faster than InlineCurrentSense class
LowsideCurrentSense current_sense = LowsideCurrentSense(185.0f, A0, A2);
// commander communication instance
Commander command = Commander(Serial);
//void doMotion(char* cmd){ command.motion(&motor, cmd); }
void doMotor(char* cmd){ command.motor(&motor, cmd); }
void setup() {
// use monitoring with serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// enable more verbose output for debugging
// comment out if not needed
SimpleFOCDebug::enable(&Serial);
// initialize encoder sensor hardware
encoder.init();
encoder.enableInterrupts(doA, doB);
// link the motor to the sensor
motor.linkSensor(&encoder);
// driver config
// power supply voltage [V]
driver.voltage_power_supply = 20;
driver.init();
// link driver
motor.linkDriver(&driver);
// link current sense and the driver
current_sense.linkDriver(&driver);
// set control loop type to be used
motor.controller = MotionControlType::torque;
motor.torque_controller = TorqueControlType::foc_current;
// SVPWM modulation type is much more efficient for hybrid stepper motors
motor.foc_modulation = FOCModulationType::SpaceVectorPWM;
// controller configuration based on the control type
motor.PID_velocity.P = 0.05f;
motor.PID_velocity.I = 1;
motor.PID_velocity.D = 0;
// default voltage_power_supply
motor.voltage_limit = 12;
// velocity low pass filtering time constant
motor.LPF_velocity.Tf = 0.01f;
// angle loop controller
motor.P_angle.P = 20;
// angle loop velocity limit
motor.velocity_limit = 20;
// comment out if not needed
motor.useMonitoring(Serial);
// current sense init and linking
current_sense.init();
motor.linkCurrentSense(¤t_sense);
// initialise motor
motor.init();
// align encoder and start FOC
motor.initFOC();
// subscribe motor to the commander
command.add('M', doMotor, "motor");
// Run user commands to configure and the motor (find the full command list in docs.simplefoc.com)
Serial.println("Motor ready.");
_delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
// iterative setting FOC phase voltage
motor.loopFOC();
// iterative function setting the outter loop target
motor.move();
// motor monitoring
motor.monitor();
// user communication
command.run();
}